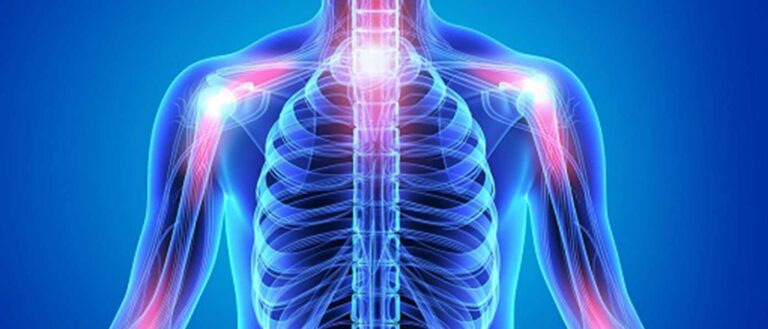
Understanding Osteoarthritis
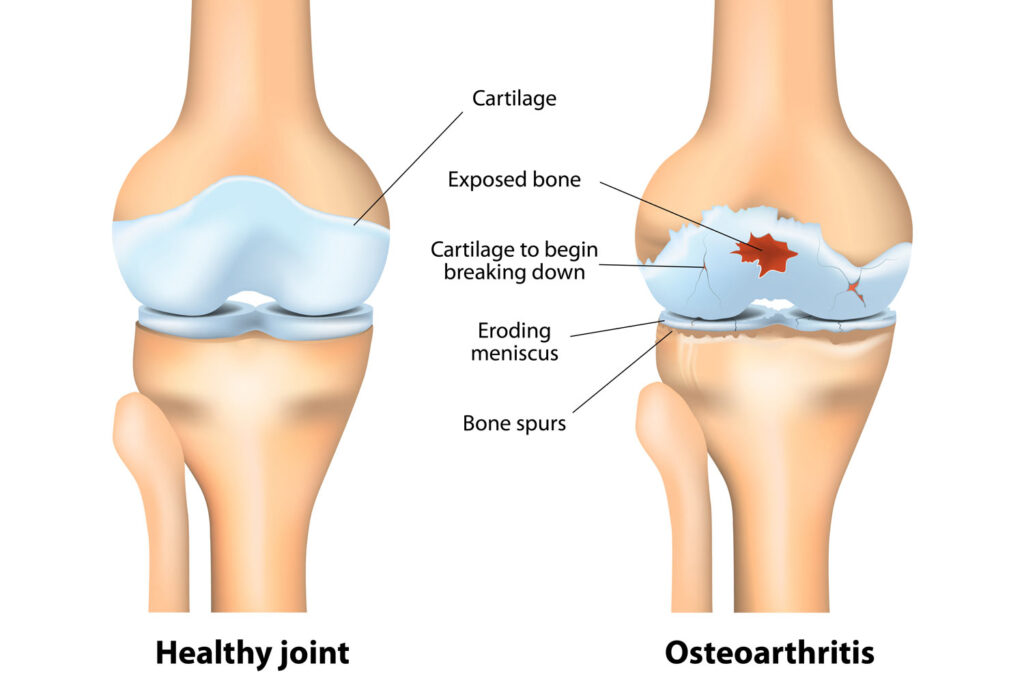
Osteoarthritis ICD 10 also known as wear-and-tear arthritis is a mechanical joint process whereby cartilage (the shock-absorbing covering on the ends of bones) degenerates. Cartilages destruction will make bones irritate and rub against each other; the same situation causes pain, stiffness, and restriction of movements. OA may occur in any joint and the most usual ones are in the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Facts on Ostearthritis:
Prevalence: Osteoarthritis is said to be one of the most disability causes in the world according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Risk Factors: these include: Aging, joint traumas, obesity, heredity, and persistent stressing of the joints.
Impact: OA has substantial influence on the quality of life, and simple operations, such as walking, bending, and lifting seem to be challenging.
The significance of ICD-10 coding in Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis ICD 10 stands as the implementing entity of a set of healthcare code used by medical professionals to categorize and code all symptoms, medical procedures and diagnoses. The conditions are assigned unique identification numbers so that they will appear consistently throughout the medical records and so they can easily be reimbursed by insurance companies.
The proper coding of osteoarthritis is very important:
- Road insurance application Medical billing
- Monitoring of epidemiology and patient statistics
- Planning procedures of treatment plans
- Supporting research and surveillance of public health data
ICD-10 osteoarthritis Codes
There are various ICD-10 codes of osteoarthritis according to:
- The place where the affected joint is situated
- And whether the condition is primary (idiopathic) or secondary
- The nature of the relationship be it unilateral or bilateral
The following are some typical ICD-10 codes of osteoarthritis:
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| M15.0 | Primary generalized osteoarthritis |
| M15.4 | Multiple joint osteoarthritis, secondary |
| M16.0 | Principal OA hip bilateral |
| M17.1 | Primary arthritis of knee, unilateral |
| M18.0 | Primary osteoarthritis, first carpometacarpal joint, bilateral |
| M19.0 | Primary osteoarthritis of other joints |
| M19.9 | Unspecified site of osteoarthritis |
Example:
In case the patients are diagnosed with primary OA in both knees, the specified code would be M17.0.
In case the patient has unspecified OA and the location of a joint was not documented, M19.9 should be coded.
Categories of Osteoarthritis
ICD-10 classification shows the type of OA as well:
Idiopathic: Primary Osteoarthritis:
Happens spontaneously and usually has no underlying reason associated with aging and natural wearing down of joints.
Secondary Osteoarthritis:
Due to another condition like joint injury, obesity and inflammatory arthritis.
Localized and Generalized OA:
Localized targets only one joint, or a few joints.
Generalized affects several joints in the body.
Risk Factors and Causes
Osteoarthritis grows with age, although some causes make it more likely to be developed:
- Age: It is most popular among adults aged above 50.
- Gender: Women predisposed to OA include overdevelopment after menopause.
- Obesity: Added weight subject the weight bearing joints to stress.
- Joint Injuries: Earlier injury such as fracture, rupture of ligaments or cartilages.
- Genetics: Family history OA.
- Occupational and Activity: Work with repeated joint motion.
Osteoarthritis Symptoms
The following are common symptoms of Osteoarthritis. OA symptoms are common and may vary by individual medical practitioners, and are, in general, exacerbated as the individual ages:
- Pain in joints with or after movement
- Morning/morning stiffness or after inactivity
- Weakness of flexibility and mobility of limbs
- Movement of the joint leads to grating sensation
- Inflammation caused swelling
- Bone spurs (osteophytes) in and around the afflicted joint
Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
A combination of the following is used to diagnose osteoarthritis:
- Medical History & Physical Examination The checking of: symptoms, range of motion, and joint tenderness.
- Imaging Tests- X-rays can show that you have lost cartilage, bone spurs, and limitation of joint space. MRI provides imagery details.
- Lab Tests -To eliminate any other form of arthritis like the rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis Treatment and Care
Even though there is no cure to osteoarthritis, the treatment can help to reduce its symptoms and consequently escalate the extent of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Being at a desired weight that would reduce the loading impacts on joints
- Low impact types of exercises such as yoga, swimming and cycling
- Preventing joint-straining activities
Medications
- Analgesics ( acetaminophen, nsaids, such as ibuprofen )
- Topical analgesics
- Inflammatory corticosteroid injection
Physical Therapy
- Increasing the body muscles on the joints
- Attracting flexibility and posture
- Some of the supportive paraphernalia such as braces or shoe inserts that can be used
Surgical Options
- Joint cleaning by arthroscopy
- Osteotomy as a realignment of bones
- Using joint replacement (arthroplasty) in severe OA
The User Role of Proper ICD-10 Coding in Osteoarthritis Treatment
Truthful ICD-10 coding does not only refer to billing: it influences the whole chain of patient care:
- Clinical Decision-making: Assists physicians in the construction of an optimal course of treatment.
- Data Analysis: Provides data for medical research; it enables data to be based in planning of public health.
- Legal Documentation: The legal documentation will provide right records in cases of disagreements.
Key Takeaways
- Osteoarthritis is a condition in which the joints deteriorate slowly and must be treated with care.
- The ICD-10 coding gives the exact codes in various forms and places of OA.
- Proper documentation, billing, and continuity of care is due to accurate coding.
- Although OA is incurable, lifestyle modifications, medication and other forms of therapy would greatly enhance the quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Osteoarthritis ICD 10 regardless of whether you are a medical coder, a patient, or a healthcare specialist, you need to understand the Osteoarthritis ICD 10 codes in order to keep correct records or plan your medication. Through adequate diagnosis, coding, and broad based treatment we will be able to ensure mobility of the patients, relief in pain and an improved quality of life.

Dr. Hamza is a medical content reviewer with over 12 years of experience in healthcare research and patient education. He specializes in evidence-based health information, medications, and chronic disease management. His reviews are based on trusted medical sources and current clinical guidelines to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. All content reviewed by Dr. Hamza is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice