Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure in the arteries. It is often referred to as “the silent killer” because it can progress without noticeable symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage, causing severe damage to vital organs.
it’s miles a continual condition that forces the heart to work harder than ordinary to circulate blood all through the body. Blood pressure is measured in (mmHg) and is represented by using two values: systolic pressure (the better value) and diastolic strain (the decrease fee).
A regular blood pressure reading is typically round a hundred and twenty/eighty mmHg. but, a person is considered to have hypertension whilst their blood strain always exceeds one hundred thirty/eighty mmHg. it’s far important to govern hypertension as it is able to cause serious health problems if left unmanaged.
Types of Hypertension:
There are 2 main types of hypertension:
Primary (critical) hypertension:
Primary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure is the most common, accounting for approximately 90-95% of all instances. It develops step by step through the years and has no unique identifiable motive.
A couple of factors can make a contribution to primary high blood pressure, which include genetics, life-style picks, and environmental factors.
Secondary high blood pressure:
Secondary hypertension is less common, making up approximately 5-10% of all hypertension cases. In contrast to primary hypertension, this kind has a clean underlying reason, and treating the underlying condition can help manipulate the high blood pressure.
Various factors can cause secondary high blood pressure, consisting of kidney sicknesses, hormonal issues, sure medicines, and different medical situations.
Causes of Hypertension:
Hypertension can be caused by:
– Genetics
– Poor diet
– Lack of physical activity
– Obesity
– Stress
– Smoking
– Excessive alcohol consumption
Symptoms of Hypertension:
Hypertension often presents without noticeable symptoms, earning it the nickname “the silent killer.” However, some individuals may experience:
– Headaches
– Dizziness
– Nosebleeds
– Vision changes

Risks and Complications:
Hypertension is a major risk factor for:
– Heart disease
– Stroke
– Kidney disease
– Vision loss
– Sexual dysfunction
Hypertension, or high blood strain, is influenced by means of various threat factors that can increase the likelihood of its development. A number of the important thing risk factors include:
Dangerous food regimen: consuming a eating regimen high in sodium (salt) and occasional in critical vitamins like potassium can make contributions to high blood pressure. Immoderate salt intake can reason the frame to retain extra water, increasing blood extent and stress at the arterial walls.
Bodily inaction: loss of regular physical pastime can cause weight gain and negatively have an effect on cardiovascular fitness, growing the threat of high blood pressure.
Weight problems: people has a higher weight, places extra strain at the heart and blood vessels, growing blood pressure.
Family history: Having a own family records of hypertension can predispose individuals to broaden excessive blood strain themselves. Genetic can play a position in how the body regulates blood strain.
Age: Blood strain has a tendency to growth with age. As people become old, the threat of high blood pressure rises.
Gender: men are much more likely to increase high blood pressure than women till menopause. After menopause, the danger will become similar for both sexes.
Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Smoking and immoderate alcohol intake can raise blood stress and damage the cardiovascular system.
Persistent Kidney sickness: The kidneys play a critical role in regulating blood strain. Any kidney disorder can cause hypertension.
Diagnosis of Hypertension:
To diagnose high blood pressure, a healthcare expert will normally observe these steps:
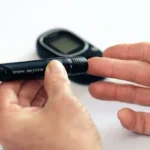
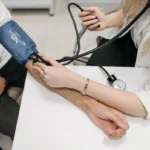
Blood strain measurement: Blood pressure is measured the usage of a sphygmomanometer, which composed of an inflatable cuff and a pressure gauge. It’s far expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and includes two numbers: systolic strain (the higher number) and diastolic pressure (the lower range).
Classification of Blood strain:
Ordinary: Systolic <a hundred and twenty mmHg and Diastolic <eighty mmHg
Elevated: Systolic one hundred twenty nine-129 mmHg and Diastolic <80 mmHg
High blood pressure degree 1: Systolic one hundred thirty nine-139 mmHg or Diastolic 80-89 mmHg
Hypertension stage 2: Systolic ≥a hundred and forty mmHg or Diastolic ≥ninety mmHg
Confirming hypertension: If the initial blood strain studying is expanded, the healthcare company will probably recheck the blood pressure on separate visits before making a prognosis of high blood pressure.
Assessment of hazard elements and symptoms: The healthcare expert will also remember different danger factors, own family records, and any symptoms that can propose secondary reasons of high blood pressure.
Additional exams: In some instances, extra checks can be ordered to evaluate the impact of hypertension on other organs and to look for underlying cause. Those exams may also consist of blood assessments, urine exams, electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), echocardiogram, or other imaging studies.
Medication for management of Hypertension:

There are several lessons of antihypertensive medications, and the selection of medicine relies upon on different factors like the affected person’s age, typical health, presence of different clinical conditions, and ability drug interactions. A few common types of antihypertensive medications encompass:
Angiotensin converting Enzyme(ACE) Inhibitor: this medicines block the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that narrows blood vessels, supporting to loosen up and widen the vessels, thereby decreasing blood strain.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): much like ACE inhibitors, ARBs work through blocking off the results of angiotensin II, main to vasodilation and lowered blood pressure.
Calcium Channel Blockers: those drugs block calcium from coming into the muscle cells of the coronary heart and blood vessels, causing relaxation of blood vessels and reduced blood strain.
Diuretics (Thiazide or Loop Diuretics): Diuretics help the body remove extra sodium and water, which reduces the volume of blood flowing via the vessels and therefore lowers blood strain.
Beta-Blockers: these medicines reduce the coronary heart charge and the force of the coronary heart’s contractions, thereby lowering blood pressure.
Alpha-Blockers: these drugs lessen nerve impulses that tighten blood vessels, main to comfortable vessels and decrease blood stress.
Vasodilators: These tablets directly relax and widen blood vessels, main to reduced blood pressure.
Useful Guide
A useful guide for hypertension patients or those who want to prevent hypertension would include the following lifestyle changes and recommendations:
Lifestyle Changes:
1. Monitor and manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
2. Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, most days of the week.
3. Follow a healthy diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
4. Reduce sodium intake: Limit sodium to less than 2,300 milligrams per day, and aim for no more than 1,500 milligrams if you’re at risk for hypertension.
5. Increase potassium intake: Potassium can help lower blood pressure; include potassium-rich foods like bananas, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes in your diet.
6. Maintain a healthy weight: If you have a higher weight, losing weight can help lower your blood pressure.
7. Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood pressure.
8. Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting can significantly lower your risk of hypertension and related health problems.
Additional Recommendations:
1. Get regular blood pressure checks: Monitor your blood pressure regularly, and work with your healthcare provider to set a target blood pressure range.

2. Take prescribed medications as directed: If you’re prescribed medication for hypertension, take it exactly as directed by your healthcare provider.
3. Stay hydrated: Drink enough water and limit sugary drinks to help manage blood pressure.
4. Get enough calcium and vitamin D: These nutrients can help lower blood pressure; include calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk in your diet.
5. Try relaxation techniques: Activities like progressive muscle relaxation, visualization, and mindfulness meditation can help manage stress and lower blood pressure.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s)
Question 1:
“Which chronic disease is often referred to as ‘the silent killer’ because it can progress without noticeable symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage, affecting an estimated 1 in 3 adults worldwide, and is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke?”
Answer:
The answer is Hypertension (High Blood Pressure). It is a chronic condition that can cause damage to blood vessels and organs, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and other complications.

Dr. Hamza is a medical content reviewer with over 12 years of experience in healthcare research and patient education. He specializes in evidence-based health information, medications, and chronic disease management. His reviews are based on trusted medical sources and current clinical guidelines to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. All content reviewed by Dr. Hamza is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice





You completed a number of nice points there. I did a search on the issue and found nearly all people will have the same opinion with your blog.
Your blog has the same post as another author but i like your better.
This information is magnificent. I understand and respect your clear-cut points. I am impressed with your writing style and how well you express your thoughts.
Just wanna remark on few general things, The website style is ideal, the topic matter is rattling good
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!
How can I find out more about it?
Please provide me with more details on the topic
I want to thank you for your assistance and this post. It’s been great.
May I request that you elaborate on that? Your posts have been extremely helpful to me. Thank you!
Sustain the excellent work and producing in the group!