Recognizing Pneumonia Symptoms
Urgent care can diagnose pneumonia with exams and tests, offering immediate care and tailored treatment plans for timely symptoms relief and recovery. When dealing with pneumonia, understanding the signs early on can make a big difference in treatment.
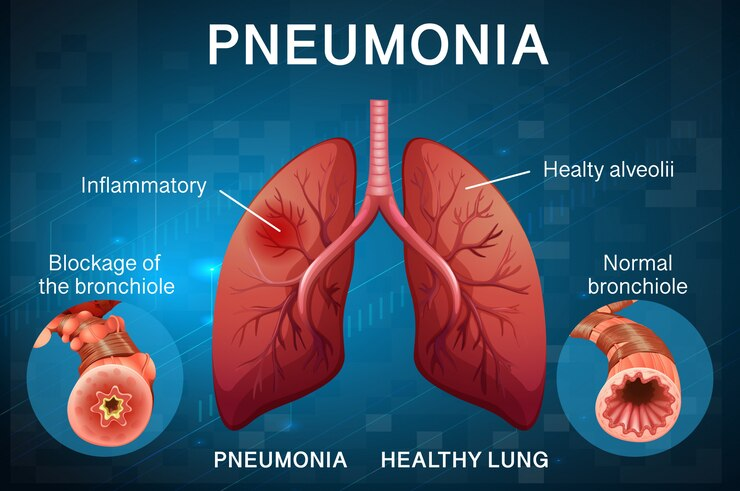
Pneumonia often starts like a common cold or flu, but it quickly intensifies and brings its own set of symptoms. People with pneumonia may feel a persistent cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing that doesn’t ease up. These signs, especially when paired with discomfort, often mean the body needs more care than usual and shouldn’t be ignored.
In many cases pneumonia can be managed at home with rest and fluids, especially if symptoms are mild. However, some cases of pneumonia require immediate attention. If you or a loved one notice these persistent symptoms, seeking timely assistance is important to rule out complications. Can Urgent Care Diagnose Pneumonia?
Can Urgent Care Diagnose Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can cause difficulty in breathing, fever, and chest pain. In order to avoid problems, prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential.
Urgent care centers provide a convenient option for diagnosing and managing pneumonia, especially when primary care appointments are unavailable or emergency room visits are unnecessary.
Does Urgent Care Test for Pneumonia?
Yes, urgent care clinics can test for pneumonia using a variety of diagnostic tools. Is it possible for urgent care to check for pneumonia?or “Can they test for pneumonia at urgent care?”, the answer is yes. These centers are equipped to diagnose and manage pneumonia efficiently.
How a Primary Care Doctor Can Help for Pneumonia
While urgent care can diagnose pneumonia, primary care physicians play a crucial role in long-term respiratory health. They ensure:
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-ups after pneumonia treatment to assess recovery.
- Preventative Care: Vaccinations, lifestyle advice, and risk reduction strategies.
- Chronic Disease Management: Managing conditions like asthma, COPD, or heart disease that can increase pneumonia risks.
How Urgent Care Centers Diagnose Pneumonia?
Urgent care clinics are equipped with diagnostic tools and experienced healthcare professionals who can assess pneumonia symptoms efficiently. The diagnostic process typically includes:
1. Medical History and Symptom Evaluation:
- Healthcare providers inquire about symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, fever, and fatigue.
- They assess risk factors such as smoking, recent respiratory infections, or pre-existing lung conditions like COPD or asthma.
- Additional Considerations: Age, immune status, and exposure history are also taken into account for a precise diagnosis.
2. Physical Examination:
- Listening to lung sounds using a stethoscope to detect wheezing, crackles, or decreased breath sounds.
- Checking oxygen saturation levels using a pulse oximeter.
- Pulse Rate and Respiratory Rate Monitoring: These vitals help determine the severity of respiratory distress.
3. Pneumonia Tests at Urgent Care:
- Chest X-ray: The most common and effective imaging test to confirm pneumonia by detecting lung inflammation.
- Blood Tests: Can help determine if the infection is bacterial or viral.
- Sputum Culture: Identifies the specific pathogen causing pneumonia.
- Rapid Flu and COVID-19 Tests: Since viral infections can lead to secondary bacterial pneumonia, these tests help in differential diagnosis.
- CT Scan (If Needed): In complicated cases, a CT scan provides a more detailed view of lung involvement.
- Pneumonia Test at Urgent Care: Patients often ask, Does urgent care diagnose pneumonia?” or Is it possible for urgent care to diagnose pneumonia? These tests are used by urgent care centers to make precise diagnosis.
How Pneumonia is Treated at Urgent Care
Treatment at urgent care depends on the severity of pneumonia and whether it is bacterial, viral, or fungal.
Bacterial Pneumonia Treatment
- Antibiotics: Most common treatment, with options like amoxicillin, azithromycin, or levofloxacin.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Fever reducers (ibuprofen, acetaminophen) and cough suppressants may be recommended.
- Hydration and Rest: Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids and get adequate rest.
- Probiotics: Help maintain gut health while taking antibiotics.
Viral Pneumonia Treatment
- Antiviral Medications: If caused by influenza, antiviral drugs like oseltamivir may be prescribed.
- Symptom Management: Hydration, rest, and fever control are key treatment components.
- Oxygen Therapy: If oxygen levels drop significantly, supplemental oxygen may be needed.
Severe Cases Requiring Hospitalization
- If oxygen levels are dangerously low, hospitalization may be needed for oxygen therapy, IV antibiotics, and close monitoring.
- Mechanical Ventilation: In extreme cases where breathing becomes critically impaired.
New Pneumonia Risk Groups & Severity Chart
Pneumonia Severity Classification
| Risk Group | Symptoms & Severity | Recommended Action |
| Low-Risk Patients | Mild cough, slight fever, normal oxygen levels | Outpatient treatment, rest, antibiotics (if bacterial) |
| Moderate-Risk Patients | Persistent fever, worsening cough, mild difficulty breathing | Urgent care visit, chest X-ray, possible oxygen therapy |
| High-Risk Patients | Severe shortness of breath, confusion, high fever, low oxygen levels | Emergency room visit, hospitalization, IV antibiotics |
| Immunocompromised & Elderly | Rapid worsening of symptoms, high mortality risk | Intensive medical care, hospital stay, ventilator support (if needed) |
How Can Pneumonia Be Treated at an Urgent Care Center?
Urgent care facilities are well-equipped to provide rapid diagnosis, basic treatment, and initial stabilization for pneumonia. They can:
- Conduct imaging tests (like chest X-rays) to confirm pneumonia.
- Prescribe medications (antibiotics, antivirals, or fever reducers).
- Recommend oxygen therapy if mild hypoxia is present.
- Offer guidance on home care and follow-up for continued recovery.
However, for severe pneumonia cases, they refer patients to hospitals or specialists for advanced respiratory care.
When to Visit Urgent Care vs. Emergency Room
It is important to determine whether urgent care is appropriate or if emergency medical attention is required.
Urgent Care for Pneumonia is Suitable If:
- Mild to moderate symptoms like persistent cough, mild shortness of breath, and fever.
- No history of severe lung disease or immunosuppression.
- The patient is able to breathe comfortably without severe distress.
- Searching “Urgent care pneumonia” suggests that patients often seek care at these facilities for mild to moderate cases.
Emergency Room is Necessary If:
- Severe breathing difficulty or blue lips/skin (cyanosis).
- Chest pain that mimics a heart attack.
- Oxygen saturation below 90%.
- High fever (above 103°F) with confusion or persistent vomiting.
- Severe Dehydration: Symptoms like dizziness, extreme weakness, or inability to retain fluids.
Final Thoughts
Urgent care centers offer a reliable option for diagnosing and managing pneumonia. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment significantly improve recovery outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does urgent care check for pneumonia?
Yes, urgent care centers conduct pneumonia tests, including chest X-rays and blood tests, to confirm diagnosis.
Can an urgent care diagnose pneumonia?
Yes, urgent care clinics have the necessary tools to diagnose pneumonia and provide treatment recommendations.
Can pneumonia be mistaken for something else?
Yes, pneumonia symptoms can resemble bronchitis, COVID-19, or even heart failure. Chest X-rays and additional tests help confirm the diagnosis.
How long does it take for pneumonia symptoms to appear?
Symptoms can develop within 24 to 48 hours in bacterial pneumonia or over several days in viral pneumonia.
Is pneumonia contagious?
Bacterial and viral pneumonia can be contagious, spreading through respiratory droplets. However, aspiration pneumonia (caused by inhaling food or liquid into the lungs) is not contagious.
What are the warning signs that pneumonia is getting worse?
- Increased difficulty in breathing.
- High fever that doesn’t respond to medications.
- Confusion or dizziness.
- Worsening cough with blood-streaked mucus.
- Persistent Chest Pain: If the pain worsens with deep breaths or movement, it could indicate pleuritic involvement.
Can pneumonia be treated at home without antibiotics?
Viral pneumonia often resolves on its own with proper rest and hydration, but bacterial pneumonia typically requires antibiotics.
Who is at the highest risk of pneumonia complications?
- older people individuals (65+ years).
- Infants and young children.
- People with chronic diseases (diabetes, heart disease, COPD).
- Immunocompromised patients (HIV, chemotherapy, organ transplant recipients).
Who can diagnose pneumonia?
Your healthcare provider can usually diagnose pneumonia by looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and reviewing test results. They will check for symptoms like cough, fever, or chest pain, which are often present in pneumonia but can also appear in illnesses like a cold or flu. Because these symptoms may look similar, pneumonia can sometimes be hard to diagnose, and people may not realize their condition is more serious than a typical cold.
If your condition lasts longer than expected or doesn’t improve, it may suggest pneumonia rather than a cold or flu. This is why healthcare providers carefully examine the signs that linger or become worse over time. They’ll use specific tests to confirm the diagnosis, ensuring that any serious cases get the right treatment to prevent complications that can happen when pneumonia goes untreated.
Where can I get a pneumonia test?
If you’re feeling sick and think you might have pneumonia or another illness, it’s best to visit a healthcare provider to ensure you get the correct diagnosis and treatment. They can evaluate your symptoms and determine whether you need a pneumonia test. If your symptoms are severe or if you’re at a higher risk for complications, it’s especially important to seek care quickly.
A healthcare provider can check if you need extra support based on your symptoms and any complications that could affect your health. Quick care is essential to help reduce risks and get you on the right path to recovery.
Can GP diagnose pneumonia?
A GP can often diagnose pneumonia by asking about symptoms and examining your chest. In some cases, tests might be required, especially since pneumonia can be difficult to diagnose due to its similar symptoms to other conditions like the common cold, bronchitis, or asthma.
What is the first test for pneumonia?
When pneumonia is suspected, the first test usually recommended is a chest x-ray. Studies show that radiography is the most effective diagnostic test for pneumonia. It is widely used in the emergency department to confirm the presence of pneumonia. While a pulmonary examination can help, it has a modest ability to predict pneumonia and is often inconsistently interpreted, even by expert examiners. Therefore, chest x-rays remain the most reliable method to diagnose pneumonia accurately.
How do you confirm someone has pneumonia?
To confirm if someone has pneumonia, a blood test is often done to check for the presence of an infection and identify the type (whether it’s caused by bacteria, a virus, or fungi). Along with this, a chest X-ray is the standard diagnostic tool used for diagnosing pneumonia. The images from the X-ray can help determine the location and severity of the infection, providing a clearer picture of the condition.

Dr. Hamza is a medical content reviewer with over 12 years of experience in healthcare research and patient education. He specializes in evidence-based health information, medications, and chronic disease management. His reviews are based on trusted medical sources and current clinical guidelines to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. All content reviewed by Dr. Hamza is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice