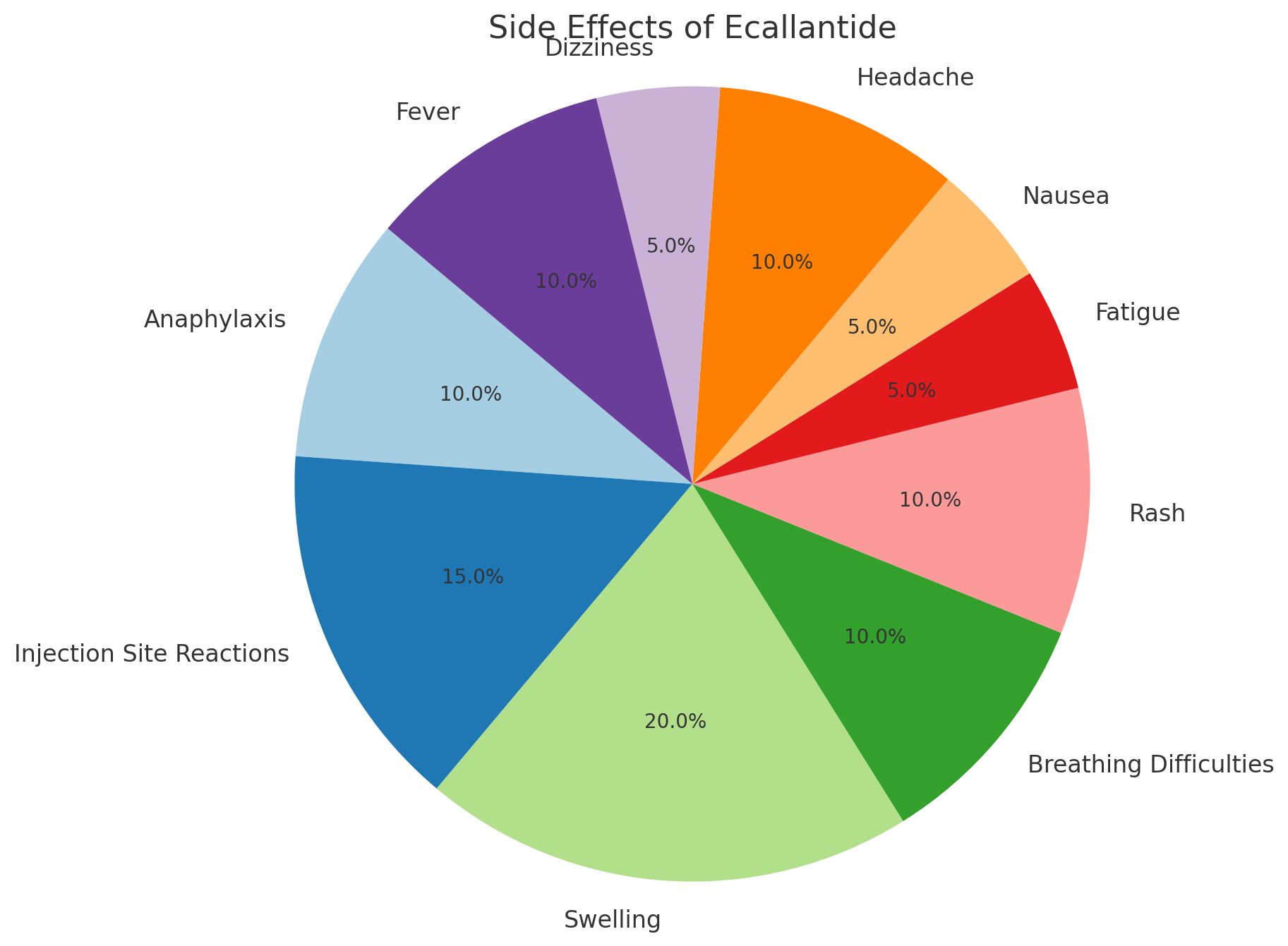
Ecallantide, sold under the brand name Kalbitor, is an FDA-approved medication for the treatment of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in acute attacks. While it can be an effective treatment, it comes with a variety of side effects of ecallantide that need to be closely monitored by healthcare providers. Below is a detailed examination of the potential side effects, categorized by their severity, and including practical advice for managing them.
Common Side Effects
Though Ecallantide helps to control HAE attacks, patients may experience several common side effects. These usually resolve as the body adjusts to the medication but should still be reported to a healthcare professional.
1. Injection Site Reactions
- Symptoms: Common are redness, swelling, itching, and tenderness at the injection site .
- Management: Cold compresses or topical ointments may relieve these mild reactions. Monitoring is key to ensuring they do not worsen.
2. Headache
- Symptoms: Moderate to severe headaches may occur following the injection.
- Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help reduce discomfort.
3. Nausea
- Symptoms: Some patients report feeling nauseated after receiving the injection.
- Management: Eating small meals and avoiding rich, heavy foods may help alleviate nausea.
4. Muscle Aches
- Symptoms: Light muscle pain, particularly throughout the injection site or in the limbs.
- Management: Stretching exercises and light movement can help relieve muscle aches.
Serious Side Effects
While less common, Ecallantide may cause serious side effects that require immediate medical attention. If any of the following condition happen, contact immediately healthcare provider.
1. Anaphylaxis (Severe Allergic Reaction)
- Symptoms: Difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, rapid heartbeat, or a sudden drop in blood pressure.
- Management: Immediate treatment with epinephrine and emergency medical care are necessary.
2. Pancreatitis
- Symptoms: Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
- Management: Hospitalization and cessation of Ecallantide may be required in severe cases.
3. Blood Clots
- Symptoms: Swelling, pain, or tenderness in the leg, redness, or warmth.
- Management: Anticoagulant treatment and close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
Long-term Side Effects
There are limited studies on the long-term use of Ecallantide, as it is generally used to treat acute HAE attacks. However, some long-term risks may include:
- Chronic immune responses leading to recurring allergic reactions.
- Organ damage such as liver or kidney issues in certain populations.
- Increased risk of pancreatitis with extended use.
Effects on Special Populations
Certain populations, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, need to be cautious when using Ecallantide. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting the medication in these cases.
- Pregnancy: The effects of Ecallantide on pregnant women have not been fully studied. Use should be considered only when necessary.
- Breastfeeding: There are no conclusive studies on Ecallantide’s effect on breastfeeding infants. Patients should weigh the risks and benefits with their healthcare provider.
- Children: Ecallantide is not recommended for patients under 12 years of age. Its safety and efficacy in younger patients have not been established.
- People with higher age: Older patients may experience more significant side effects due to age-related kidney, liver, or heart conditions. They require careful dose adjustment and monitoring.

When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
Always seek medical advice if experiencing any serious side effects. Some symptoms may indicate underlying conditions worsened by Ecallantide treatment.
• Severe dizziness
• Fainting or loss of consciousness
• Chest pain or discomfort
• Severe skin reactions
Managing Side Effects
Managing side effects involves both proactive and reactive approaches. Mild side effects like headaches and nausea can often be managed with over-the-counter medications, while more severe reactions require medical intervention.
• Injection site reactions can often be reduced by proper administration techniques and rotation of injection sites.
• Headaches and muscle aches can be managed with non-prescription pain relievers.
• Nausea can be alleviated with dietary changes and medications as prescribed by your doctor.
Monitoring and Precautions
Monitoring patients closely, particularly during the first few injections of Ecallantide, is crucial to ensuring safety. Higher age patients or those with kidney or liver conditions should be monitored more frequently.
Interactions with Other Medications
Prescription Medications
Ecallantide may interact with certain prescription drugs, including those used to treat:
• High blood pressure (ACE inhibitors)
• Heart conditions
• Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
Over-the-Counter Drugs
Consult a healthcare professional before using over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications or pain relievers, as these may interfere with Ecallantide’s effectiveness.
Alcohol or Tobacco Interactions
Alcohol can exacerbate dizziness and fatigue, while tobacco may affect the body’s inflammatory response, possibly reducing the drug’s effectiveness.
Food Interactions
There are no significant food interactions reported with Ecallantide, but eating well-balanced meals may help in faster recovery from acute HAE attacks.
Overdose Symptoms and Treatment
While overdose is rare, symptoms may include severe dizziness, fainting, or difficulty breathing. In case of overdose, seek immediate medical attention. Treatment typically involves supportive care, including fluids and monitoring of vital signs.
Precautions Before Using Ecallantide
Ecallantide, known by its brand name Kalbitor, is a plasma kallikrein inhibitor used to treat acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE). Though the drug can significantly help manage the swelling, pain, and inflammation associated with HAE, it is important to be aware of various precautions that may affect the treatment’s safety and effectiveness.
Before using Ecallantide, several factors need to be considered to ensure the patient’s well-being. Below are important precautions that must be discussed with your healthcare provider.
1. Allergies to Medications or Substances
Patients must disclose any known allergies to medications or substances. Ecallantide may trigger serious allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening. It’s essential to review your medical history, especially any allergies to:
- Other medications like antihistamines or kallikrein inhibitors
- Foods, preservatives, or dyes.
| Symptoms of Allergic Reactions | Severity |
| Swelling of the face or lips | High |
| Difficulty breathing | Severe |
| Skin rash or hives | Moderate |
| Itching or redness | Mild |
Patients with a history of anaphylaxis to similar treatments should undergo close monitoring during the administration of ecallantide. Proper testing or skin tests may also be recommended before using the drug.
2. Kidney or Liver Conditions
Patients with kidney or liver disease require special care when using Ecallantide. Both organs play a crucial role in metabolizing and excreting the drug. In cases of kidney impairment or liver dysfunction, the drug’s breakdown may slow down, leading to higher concentrations in the body, which can increase the risk of adverse reactions.
For patients with compromised kidney or liver function, the dosage of Ecallantide might need to be adjusted. Daily blood tests can also be required to observe how well these organs are functioning during the treatment.
Key considerations for patients:
- Inform your doctor about any previous liver disease (like cirrhosis or hepatitis) or kidney disease.
- Regular monitoring of kidney function tests like creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) may be necessary.
| Condition | Impact on Treatment |
| Kidney Disease | May require dosage adjustments to prevent drug accumulation. |
| Liver Disease | Can impact the body’s power to process and eliminate the drug. |
3. History of Heart Problems
Patients with a history of heart problems, such as arrhythmias, heart failure, or hypertension, should exercise caution when using Ecallantide. The drug has been associated with side effects like tachycardia (rapid heart rate) and chest discomfort. Those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions may be more vulnerable to these reactions.
· Arrhythmias: Individuals with irregular heartbeats might experience exacerbation due to medication interactions or fluid retention.
· Hypertension: High blood pressure can be worsened by medications that affect the body’s vascular system.
Important steps:
- Discuss any heart-related issues with your doctor before starting Ecallantide.
- Close monitoring of your heart rate and blood pressure may be needed during and after administration of the drug.
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Considerations
The safety of ecallantide during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been fully established. Pregnant women should only use the medication if the potential benefits outweigh the risks to the fetus. Since ecallantide can cross into breast milk, breastfeeding mothers should also be cautious.
Pregnancy Considerations
- First Trimester: The potential for teratogenic effects (birth defects) is highest during early pregnancy, though no direct studies confirm such risks for Ecallantide.
- Second and Third Trimester: While the risk may be lower in later trimesters, fetal health monitoring is essential.
- Breastfeeding: Since it’s unknown whether Ecallantide is excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when administering the drug to breastfeeding women. It is advisable to either discontinue the drug or breastfeeding, depending on the importance of the medication to the mother.
Monitoring for Pregnant and Nursing Women:
- Frequent ultrasounds and fetal monitoring may be recommended for pregnant women taking Ecallantide.
- Lactation consultants may help assess whether breastfeeding can safely continue while on the medication.
| Category | Risk Level |
| Pregnancy (Category C) | Use only if benefits outweigh risks. |
| Breastfeeding | Unknown if excreted in human milk; exercise caution. |
Summary of Precautions
In summary, Ecallantide should be administered with caution, especially for patients with allergies, kidney or liver conditions, heart problems, and during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Patients must maintain close communication with their healthcare provider to manage risks and ensure the safe use of the medication.
If you have any doubts or concerns regarding the use of Ecallantide, always consult with your doctor to discuss your health condition and ensure you receive the best care tailored to your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
1. Can I use Ecallantide during pregnancy?
Ecallantide’s effects on pregnancy are not well studied. It can only be used if absolutely necessary and prescribed by a doctor.
2. if I miss a dose what should we do?
Ecallantide is generally used during acute HAE attacks, so missed doses are uncommon. If scheduled doses are part of your treatment, follow your doctor’s instructions on how to manage missed doses.
3. Are there food or drug interactions with Ecallantide?
Yes, discuss any other medications, including over-the-counter drugs, with your healthcare provider before using Ecallantide. There are heavy interactions with food, alcohol, and other medications.
4. How is Ecallantide stored?
Ecallantide should be stored in a refrigerator and not frozen. It should be kept in its original container, away from light and out of reach of children.
5. Can I take Ecallantide with other medications?
Ecallantide may interact with medications such as:
- ACE Inhibitors: These are often used for high blood pressure and heart disease but may worsen swelling in HAE patients.
- C1 Esterase Inhibitors: If you’re using a C1 esterase inhibitor for HAE, talk to your doctor about how to coordinate treatments.
- Antihistamines and Corticosteroids: These drugs may be prescribed to help manage allergic reactions or side effects but should be used under medical supervision when combined with Ecallantide.
Always consult your doctor about any medications you’re currently using to ensure that combining them with Ecallantide is safe.
6. Can I drink alcohol while using Ecallantide?
There is limited information about alcohol interaction with Ecallantide. However, it’s generally a good idea to avoid alcohol while using medications for serious conditions like HAE, as alcohol can sometimes exacerbate side effects like dizziness, nausea, or headaches.
7. How should I store Ecallantide?
Ecallantide should be stored in a refrigerator between 2°C and 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and should not be frozen.Store in original packaging to protect it from light. Do not use Ecallantide if it has been left at room temperature for an extended period or if the solution appears cloudy or contains particles.
8. Can children use Ecallantide?
Ecallantide is approved for use in children over the age of 12. However, its safety and efficacy in younger children have not been well established. Always contact a pediatrician before taking treatment.
9. Can older patients use Ecallantide?
Older patients can use Ecallantide, but they may be more susceptible to side effects, particularly if they have existing liver, kidney, or heart problems. Dose adjustments may be necessary for older individuals, and frequent monitoring is recommended.
10. if I overdose on Ecallantide what should i do?
In case of overdose, seek immediate medical attention. Overdose symptoms may include serious dizziness, fainting, or difficult breathing. Supportive care, including monitoring of vital signs, will likely be required in a medical facility.
11. What are the signs of an allergic reaction to Ecallantide?
Allergic reactions can include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, hives, and rapid heartbeat. If you experience any of these symptoms after receiving an Ecallantide injection, seek emergency medical attention right away.
12. Can I drive or operate heavy machinery after taking Ecallantide?
Due to potential side effects such as dizziness, fainting, or headache, it’s recommended to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after receiving an Ecallantide injection until you know how the medication affects you.
13. What is the long-term impact of using Ecallantide?
Ecallantide is particularly used for acute attacks of HAE and not for long-term, ongoing treatment. While long-term side effects are rare, repeated use over time could potentially lead to increased immune responses or allergic reactions. Always follow up regularly with your healthcare provider for long-term management plans.
14. Is it safe to use Ecallantide while breastfeeding?
There are no conclusive studies on the safety of Ecallantide while breastfeeding. Consult your healthcare provider to weigh the potential risks and benefits before using Ecallantide during breastfeeding.
15. What should I do if I experience serious side effects?
If you experience any serious side effects, such as anaphylaxis, severe swelling, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention. Contact your doctor right away if you notice severe dizziness, fainting, or symptoms of pancreatitis (severe abdominal pain).
16. Can I take Ecallantide if I have food allergies?
Yes, but you must inform your doctor about any food allergies, as Ecallantide may cause allergic reactions.
17. Will Ecallantide affect my kidneys?
Ecallantide can affect the kidneys, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions, so regular monitoring may be required.
18. Can I take ecallantide if I have a mild food allergy?
It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about any allergies, even to foods, as some inactive ingredients might trigger a reaction.
19. What should I do if I experience an allergic reaction to ecallantide?
If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as swelling, difficulty breathing, or hives, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
20. How does liver disease affect the dosage of ecallantide?
Liver disease can slow the breakdown of the medication, potentially increasing side effects. Dose adjustments may be required based on liver function tests.
Conclusion
Ecallantide is a critical treatment for patients suffering from hereditary angioedema, but it carries risks, including serious side effects like anaphylaxis and pancreatitis. Patients must work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor and manage these risks effectively. Researchers and healthcare providers continue to study the drug’s long-term impact, but proper use under medical supervision minimizes the chance of adverse effects.
For more information, refer to studies published on the National Institutes of Health website or consult your healthcare provider.