What is Respiratory Diseases?
A respiratory diseases, also known as lung disease, refers to any condition that disrupts the normal functioning of the respiratory system, making breathing difficult. This system encompasses the organs and tissues involved in gas exchange, including the lungs, airways (trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles), and muscles of the chest wall.
Types of Respiratory Diseases:
- Airway diseases: These conditions obstruct or narrow the airways, making it difficult to breathe. Examples include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchiectasis.
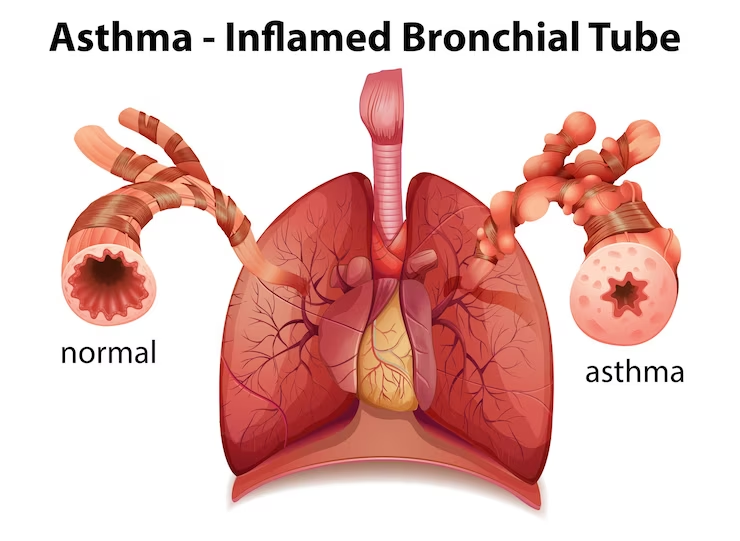
- Asthma: A chronic inflammatory condition causing airway hyperresponsiveness, leading to recurrent episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive disease characterized by airflow limitation, often caused by smoking.
2. Lung parenchymal diseases: These diseases directly affect the lung tissue, hindering its ability to transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently. Examples include Pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer.
- Pneumonia: an infection causing inflammation of the lung tissue, often with symptoms like fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
- Lung cancer: uncontrolled cell growth in the lungs, often presenting with persistent cough, weight loss, and chest pain.
3. Vascular diseases: These conditions impact the blood vessels in the lungs, disrupting blood flow and gas exchange. An example is pulmonary embolism.
Causes of respiratory diseases:
- Smoking: The leading cause of respiratory disease, smoking damages the lungs and increases the risk of various conditions.
- Air pollution: Exposure to pollutants like secondhand smoke and air particulates can irritate the lungs and contribute to respiratory problems.
- Infections: Viruses, bacteria, and fungi can cause respiratory infections like the common cold, pneumonia, and bronchitis.
- Occupational hazards: Exposure to dust, chemicals, and fumes in certain workplaces can lead to occupational lung diseases.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to certain respiratory diseases like cystic fibrosis.
Symptoms of respiratory diseases:
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Coughing, with or without phlegm (mucus)
- Wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing
- Chest tightness or pain
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss

Prevention and Treatment:
- Smoking cessation is crucial for preventing and managing respiratory diseases.
- Avoiding air pollution and using air purifiers can help minimize exposure to harmful triggers.
- Vaccination against certain respiratory infections, like influenza and pneumonia, is recommended.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing respiratory diseases effectively. Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and may include medications, inhalers, oxygen therapy, and even surgery in some cases.
Conclusion:
Respiratory diseases are a significant global health concern. By understanding the different types, causes, and symptoms, we can take preventive measures and seek prompt medical attention when necessary. Remember, early diagnosis and proper management are key to living a healthy and fulfilling life despite respiratory challenges.
