Introduction
Gastrointestinal (GI) diseases encompass a wide range of disorders affecting the digestive system. From mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions, these disorders can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. These ailments can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. So gastrointestinal disorders require a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, dietary experts, and lifestyle counselors to improve the overall quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
Common Gastrointestinal Diseases
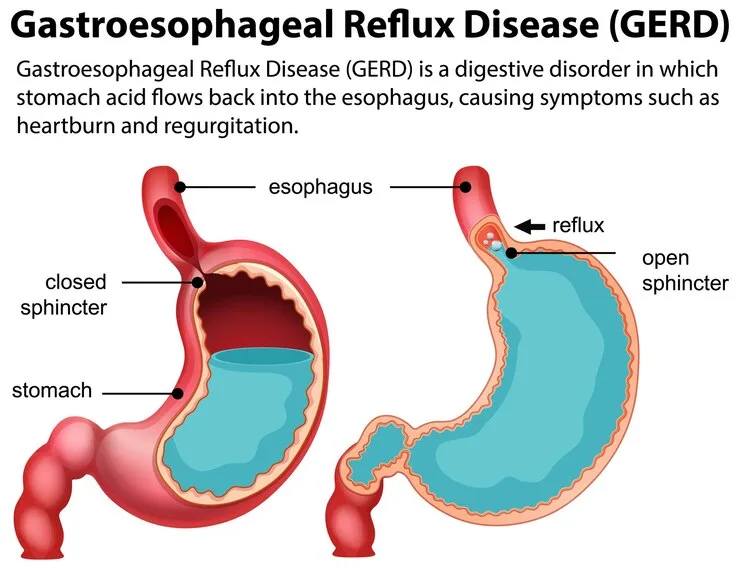
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Characterized by chronic acid reflux, GERD occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a functional disorder of the GI tract, leading to abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits without any visible signs of damage.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, IBD involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract, leading to severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue.
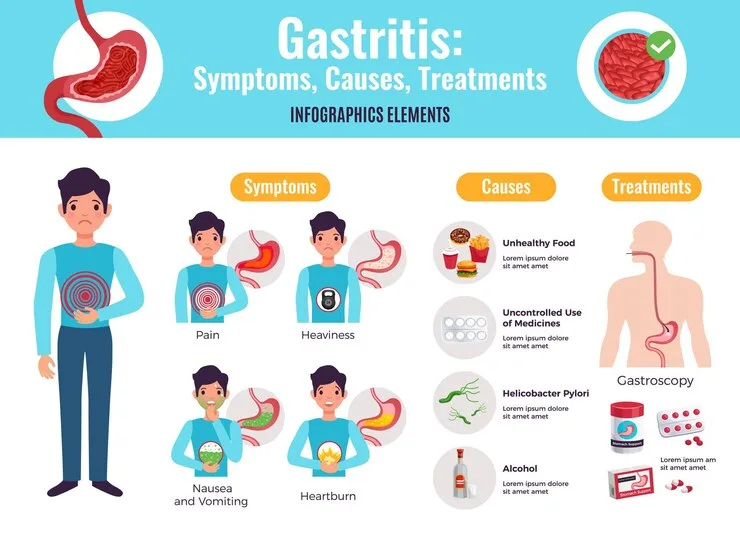
- Gastritis: Gastritis refers to the inflammation of the stomach lining, often caused by infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria, excessive alcohol consumption, or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Gallstones: These are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, leading to intense abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, especially after meals high in fat.
Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Diseases
GI diseases manifest through a myriad of symptoms, often overlapping with other conditions.
Common symptoms include:
- abdominal pain
- Bloating
- diarrhea
- constipation
- Nausea
- vomiting
- rectal bleeding
- weight loss
- Fatigue
- changes in bowel habits
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of GI diseases vary depending on the specific condition. Factors contributing to these ailments include:
- Diet: Consumption of high-fat, low-fiber foods can increase the risk of developing GI disorders.
- Genetics: Some GI diseases, such as IBD, have a genetic predisposition.
- Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate symptoms of GI disorders like IBS and GERD.
- Infections: Bacterial and viral infections can lead to gastritis, gastroenteritis, and other GI ailments.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as NSAIDs and antibiotics, can irritate the GI tract and contribute to the development of GI diseases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing GI diseases often involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These may include:
- Endoscopy: A procedure that allows the doctor to examine the inside of the digestive tract using a flexible tube with a camera.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can provide detailed images of the GI tract to identify abnormalities.
- Blood tests: Assessing blood markers can help diagnose conditions like anemia, inflammation, and infection.
Treatment Options
Treatment for GI diseases aims to alleviate symptoms, control inflammation, and prevent complications. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms.
- Dietary changes: Avoiding trigger foods, increasing fiber intake, and maintaining a balanced diet can help manage GI disorders.
- Lifestyle modifications: Managing stress, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are essential for overall GI health.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove damaged tissue, repair the digestive tract, or remove gallstones.
Conclusion:
Gastrointestinal diseases pose significant challenges to millions of people worldwide, affecting their daily lives and overall well-being. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for these conditions, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their GI health effectively. Early detection, proper medical care, and lifestyle modifications are key to living a fulfilling life despite these challenges.